Did Staghound Armored Car See Service In Sicily?
British tanks and armored cars 1939-1945
Models by type
- British Alphabetize
Cruiser tanks
- Comet, Cruiser Tank, A34
- Cromwell, Cruiser Mk.Eight, A27
- Cruiser Mk.I, A9
Infantry tanks
- Churchill NA 75
- Churchill, Infantry Tank Mk.IV, A22
- Infantry Tank A.11 Matilda
- Matilda II, Infantry Tank Mk.II, A12
- Valentine, Infantry Tank Mk.III
Medium tanks
- Vickers Medium Mk.D
- Vickers Medium Mk.I & Mk.Two
- Vickers Medium Mk.III
Light tanks
- Lite Tank (Airborne) M22 Locust
- Tetrarch, Lite Tank Mk.VII, A17
Tank destroyers
- Churchill Gun Carrier, A22D
- Sherman VC Firefly
Tankettes
- Loyd Carrier
- Universal Carrier
Flame-thrower vehicles
- Sherman Crocodile
Armored cars
- Bison Mobile Pillbox
- Guy Light Tank (Wheeled)
Funnies
- Canal Defense force Lite (CDL) Tanks
- Churchill AVRE
- Churchill Crocodile, A22F
- Sherman BARV
Other Vehicles
- Churchill ARV Mk. I & Mk. Two
- Morris-Commercial C9/B Cocky-Propelled 40mm Bofors
- Sherman 'Tulip' Rocket Firing Tanks
Vehicles
- Vauxhall B.T. Three-Quarter track Traclat
AT Weapons
- Rifle, Anti-Tank, .55in, Boys "Boys Anti-Tank Rifle"
- Glutinous and Magnetic Anti-Tank Weapons
Prototypes
- 40RBL78 MA Field Gun
- A.eleven.E.1 Infantry Tank Matilda Prototype
- Assault Tank, A33 "Excelsior"
- Blackness Prince, Infantry Tank, A43
- Churchill Mk.Three with 'Ardeer Aggie' Mortar
- Comet, Cruiser Tank, A34* (Star)
- Gerrey Automobile Gun Motor Vehicle
- Heavy/Assault Tank T14
- Johnsons Calorie-free Tropical Tank
- Kahn'due south Obstacle Brawl / Rolling Fortress 'Tank'
- Morris-Martel Tankettes
- Praying Mantis
- Smeaton Sochaczewski Carrier
- The Bechhold Tank
- TOG 300G
- TOG Amphibian
- TOG Citadel
- Tortoise, Heavy Assault Tank, A39
- Valiant, Infantry Tank, A38
- Vickers Amphibious Light Tank A4E3 L1E3
- Vickers No. i & No. 2 Tanks
Fakes
- Walmington-on-Sea APC (April Fools)
British related tactics articles
- British Somaliland Campaign 1920
- British Tank Losses March to May 1945: The State of war in North West Europe
- Campaigns and Battles in East Africa – The North, British and French Somaliland
- Effectiveness of Tactical Air Strikes in World State of war Ii – "Tank busting"
- Esigenza C3 – The Italian Invasion of Malta
- Operation Spotter – The First Centurion Trials 1945
British related tech articles
- British work on Zimmerit
Introduction
While the British Empire was depending foremost on its navy to defend its interests, it likewise had modern and efficient shipping, and a pocket-sized ground forces, simply very well equipped and trained. Its armored forces were not at all numerically equal to France or Nazi Deutschland, but qualitatively of good level. This was the case mostly thanks to a booming consign product in the thirties (mostly Vickers) and many tests, exercises and authorship of the idea of mechanized warfare (in fact the basis on which the Blitzkrieg was founded), with revolutionary concepts such as the Carden-Loyd tankette, or the adoption of the Christie suspension for its cruiser tanks.
The BEF (British Expeditionary Force) in May, 1940
In 1939, besides the colonial forces stationed around the earth, mainly made upwardly of infantry and artillery, the heavy mechanized forces were included in the British Expeditionary Force commanded by Lord Gort, formed in 1938, and landed in French republic soon afterwards the announcement of war on September iii. Reduced in number (1 tenth of the Centrolineal forces, France, Belgium, Holland, Denmark included), but of very high gainsay value, the BEF included 158,000 men, arrived in five weeks, with 25,000 vehicles, artillery and support. Final deployment was completed in May 1940, in 10 divisions, assisted by 500 units (approximately 400,000 men). The bulk of the forces were assigned to the French-Belgian border, only some units went and stood behind the Maginot Line.
These forces were highly mechanized and consisted mainly of trucks and arms tractors, armored cars and tanks, classified co-ordinate to the custom of the time, in cavalry tanks (Cruisers), Scouts (Light) and Infantry. But considering of the turn of events, most of this hardware was lost on the the style to the Dunkirk beaches. Only the Matilda seemed to resist the German onslaught, when counter-attacking at Amiens, merely the Germans 88 mm (3.46 in) Flak guns, superior coordination and air power definitely broke this mettlesome just futile endeavor.
The African Campaign (1940-43)
Many of the models already developed or under development in 1940 entered mass-produced, with many versions and variants until the end of the war. However, some new tanks appeared due to the precious war experience gathered, which ultimately led to the awesome Centurion, maybe the world'southward first modern MBT or "Chief Battle Tank". The best suited tanks for armored offensive appeared to be of the cruiser gender. After the Cruisers Three and IV, a complete redesign of the suspension, using for the start time the Christie system, led to the pattern of the Mark V Covenanter and the Mark 6 Crusader.
The latter gained fame in the N African campaign, only it was obsolete by 1943 and new models had arrived: The Cavalier, Centaur and, near famous, Cromwell (Mark 7), all equipped with the new vi pdr (57 mm/ii.24 in) antitank gun, improved engine and armor.
When the African campaign started, the British armored force was left with 2d-rate tanks, most of most obsolete models, like the Calorie-free Tanks Mk.Ii/3, Mk.Five and Mk.VI and tankettes, and the obsolete Vickers Medium Mark II. In that location were also a few Cruisers Mk.2/IIIs. By 1940, every bit the Italian threatened Egypt from their Eastern African colonies and Libya, some armored reinforcements were sent, and nearly all available tanks when, in September 1940, the Germans ceased their air offensive over Britain.
At the aforementioned time, production was re-centered effectually a few models: The infantry tank Matilda 2, the Cruiser tank Mk.IV, and the freshly arrived Valentine. Since local Italian armor was not really impressive, the bulk of the British light tanks had been based in North Africa and in the eastern colonies (Singapore, India, Burma). By the fall of 1940 and until the autumn of 1941, a not well-known offensive saw these second-rate tanks, aslope many British and Australian armored cars, fighting off the Italians in Eritrea and Somaliland (East-African campaign).
But by the beginning of 1941, afterwards a series of humiliating defeats, the Regio Esercito had been pushed dorsum and even chased out from Libya. The British forces had reached Tobruk and now threatened the Italian presence in Africa itself. Hitler, unwilling to let his ally lose this precious position against British primary eastern merchandise roads and supply lines, sent two divisions, the core of a future "Afrika Korps", under the command of ane of the most praised German language generals in history, Erwin Rommel. The year 1941 was a complete contrary of the initial successes of the British army, which was pushed back all the way to Egypt. By mid-1942, several epic battles, were tanks played a vital function, contributed to irksome down the Italo-German language advance, until the turning bespeak at El Alamein.
By mid-1941, the British ground forces had received two new tanks. First wasthe brand new Crusader, with a Christie suspension which gave, on the flat battlegrounds of the Due north African theater, stunning performances. Simply speed itself was not sufficient, especially confronting High german tactics using bait forces and ambushing antitank units. The second tank was not British but American, on insisting British asking. It was a medium tank with powerful armament -but in an awkward configuration- , good armor and mobility. Nicknamed "the Iron cathedral", the M3 served every bit the Lee in U.s.a. service, and the Grant in British service, with distinctive modifications. Despite its shortcomings, information technology was dependable and contributed to stopping the German advance literally miles from the Nile, at El Alamein, a remote railroad junction. But most of all, the future "Desert Rats" were now led by a shortly iconic figure, Bernard Montgomery.
By the fall of 1942, the first British M4 Shermans arrived en masse through Alexandria harbor, but the bulk of VIIIth forces however comprised M3 Grants, M3 Stuarts, Crusaders, Cruiser Three-IVs, Matildas and Valentines. All these forces were patiently and advisedly gathered for the great African offensive of El Alamein (second battle), planned past Montgomery in October-November 1942. At the aforementioned time, the offset The states Regular army western front delivery of the state of war came in French Algeria, with operation Torch. This behemothic pincer movement was designed to deliver the coup de grace to the Afrika Korps and the remainder of the Italian forces, now retiring to Tunisia.
The Tunisian campaign was nada simply a though and bloody thing. Tunisian muddy winter combined with a stiffened and well-ordered fighting retreat by hardened Axis troops was not what the Allies expected, and the inflow of general Kesselring with fresh reinforcements, including the brand-new Tiger tank, further increased the Centrolineal disarray. As a response, British armor received new anti-tank guns, just to lead the assault, they also received the heavy Churchill tank, slow but extremely resilient and versatile.
The last Crusaders had been phased out, and early versions of the Valentine had been converted with success into the Bishop SPG. At present obsolete Grants were sent to the Far Due east. They would get on to have a brilliant fighting career in Burma, until 1945. The Condescending, Centaur and Cromwell, all based on the same requirements and very similar, arrived in express numbers. Their new high-velocity gun and reliable engine proved more than a match for many aging Panzer III and IVs.
The Italian Campaign (1943-45)
The surrender of all Axis forces in Tunisia came in May 1943. The Allies, however, had not succeeded in completely destroying Kesselring's army, which retreated in skilful society to Sicily. The Sicilian entrada, from July to August 1943, saw the all-encompassing utilise of The states Lend-Lease vehicles to compensate for the British losses, mainly Monty'due south VIIIth ground forces, comprising M2/M3 half-tracks, jeeps, trucks, M5 Stuarts, besides as M3 derived self-propelled artillery (US-built Priest and Canadian-congenital Sexton). During the previous desert operation, Lend-Lease Jeeps and Chevrolet trucks, modified and heavily armed, served with the famous LRDG (Long Range Desert Group), using effective hit-and-run tactics. The side by side campaign, starting in Italy in September at Salerno and Taranto saw a growing number of Canadian-built tanks, mainly Universal Carriers and the Sexton SPG. Now the mainstay of the British tank strength, apart from the Shermans and Churchill, were the Cruiser Vii ("C" models) and afterward versions of the Valentine. Before long subsequently these landings, a new Italian regime was formed, which decided to put Mussolini in arrest and quickly entered peace talks with the Allies. Merely, despite the defection of Italian troops, the offensive reached a standstill. General Kesserling was able to put a very sturdy resistance, helped by his hardened troops, some reinforcements and the Italian landscape. The Italian campaign dragged on until the fall of 1945.
D-Day and the European campaign (1944-45):
Before D-Day, the only attempted landing in occupied France had occurred on 19 Baronial 1942. This was a complete failure, with a heavy price which was more often than not paid by Canadian troops. This was also one of the start deportment of the new Churchill tank. Already adult in 1941, the Churchill looked obsolete, and it was plagued by teething problems. At Dieppe, none of these heavy tanks made it farther than the beach, easy prey for the German artillery at indicate-bare range. The problem was non in the tank, just in the very stuff that composed the beach, tiny chert which clogged into the drivetrain and tracks. The Churchills were doomed. Simply this tank would prove its value in a matter of weeks in North Africa and particularly Tunisia,. When all its defaults were corrected, information technology concluded up as a very fine armored vehicle. Information technology was extremely sturdy, roomy, reliable, and highly adaptable, and information technology could climb slopes impossible for whatsoever other Allied model. Information technology became the staple of the Royal engineers for every duty imaginable, from D-Day to 5-Day.
The bulk of the British tank strength during D-Mean solar day was fabricated of U.s.a.-built Sherman tanks. The British were not long to grasp the potential of this tank and quickly attempted a modification of their own, the Firefly. This was basically an up-gunned version, fitted with the long-barrel, high-velocity QF 17-pdr (76.2 mm/3 in), the British perfect "tank killer", capable of knocking out any German tank of the day. It was used in conjunction with other models and proved really up to the chore during the operations in the Normandy bocage and heavy fighting around Caen. The US devised their own upgunned version, the 76(w), which appeared not long after and became the adjacent upgrade of all Sherman versions.
The 2d most important British tank deployed was the Cromwell. Derived from the long line of "cruisers" and equipped with the same engine as the legendary Spitfire (the Rolls-Royce Shooting star), the Cromwell was faster than the Sherman, merely also lower, and equipped with the largely available and very efficient QF 6-Pdr (57 mm/ii.24 in) gun. However, it was cramped and the minor hatches likewise oftentimes condemned the crews to burn live inside the tank. The Cromwell was chiefly used for training, and only equipped the seventh Armored Segmentation and other elite specialized units, like the reconnaissance units attached to the Guards Armored Partition and 11th Armored Division.
Other important AFVs deployed at D-Day were the self-propelled howitzers, M7 Priest and the Canadian Sexton. Indirect fire could exist provided speedily thanks to these vehicles, which turned out to as well be efficient troop transports. And then much so, that many other turretless vehicles were chosen for the job, summarily called "Kangaroo". Only these converted vehicles were all open-topped. The unique SPG designed to operate as a tank hunter was the 17-Pdr Archer, based on the Valentine chassis. Around 600 were produced in 1944, and they operated in France, Holland, Germany and Italy. These were characterized by a rearward-firing configuration.
The A30 Challenger (Cruiser Mark VIII) made its debut in France in the summertime of 1944. It was introduced with the new high-velocity 17 pdr (76.two mm/3 in) QF AT gun, capable of dealing with German Panzer IVs and Panthers. However, its development took time, and the Firefly appeared cheaper to convert in numbers. So despite its advantages (information technology was faster and agiler), the costly and complex Challenger never saw action before July and August 1944, when the mulberries were operational, and but 200 were congenital, equipping British elite units, also as Czech and Smoothen ones.
Both concepts of tank hunter and cruiser tank were reunited in a unmarried bundle, the Comet, first introduced by early 1945. The Comet was basically a Cromwell re-equipped with a specially adapted version of the deadly QF-17 pdr. An impressive parcel of speed, armor and firepower, which represented the top of British feel facing German tanks. But it was not the last "cruiser". As soon as 1943, the general Staff asked for a "Heavy Cruiser" (A41), which could withstand a directly hit from a High german 88, be active like the Comet and Cromwell, all the same be armed with an improved version of the QF 17-pdr and stay inside the 40-tons limit to permit transport by the lorries. A mock-upwardly was built in May 1944, with prototypes in early on 1945 after many revisions. It is said that three pre-serial Mk.I Centurion prototypes were sent to Deutschland before V-day, simply the armistice was signed before they could participate in any activeness. However, they had a great postwar career and pioneered the "primary battle tank" nosotros know today.
Armoured cars
Daimler Dingo
With most 6,400 machines produced in several sub-versions until 1945, the Dingo was one of the all-time armored reconnaissance four×4 vehicles produced in the world. Nearly 400 served during the entrada of France in the 1st Armored Partition and the Northumberland Fusiliers; and in many theaters later on.
Humber Light Reconnaissance Car
Near 300 of these armored armored automobile were produced by the Rootes Group (Humber) and served with the BEF. These vehicles had a Boys anti-tank rifle and a Bren gun. After the Fall of French republic, 3600 more would be produced.
Older models
-In that location were withal ww1 vintage or 1920-24 pattern Rolls-Royce models in use in North Africa, peculiarly in Great socialist people's libyan arab jamahiriya and Due east Africa
-The rare Vickers Crossley 4×4 (model 25) was produced for Nihon, whereas 100 "Indian pattern" were used past the Raj of India and the vi×vi Marker I was withal during the war for preparation (to come up). Virtually thirteen IGA-1s 6×half-dozen were besides used by the Estonian defence Forces in WW2 and the model 26 4×4 by Argentine republic.
-Guy Armoured Car: Only 101 of the "pre-production" prototypes for the famous Humber were built by Sydney Guy at Wolverhampton in 1939. But four went with the BEF, all captured, the balance were used at home for training.
-Lanchester vi×4: A rather rare 6×6 model adult in 1928 (34 congenital) and used overseas during ww2 (Malaya) and at home for training. Relatively similar to the Vickers-Crossley.
New ww2 models
-Humber armored auto: One of the well-nigh successful ww2 armored cars. Adult from the Guy in 1940, 5400 were produced up to 1945. Armament was variable but in full general a couple of a heavy Besa and light machine guns. Used equally a standard for basis reconnaissance on all fronts.
-AEC Armoured Machine: A 4×4 monster built during the war and sturdy enough to sport the turret of the Valentine tank. It was one of the primeval example of a wheeled tank during ww2.
-Coventry Armoured Car: A belatedly (1943) ww2 attempt to design a standard wheeled armored car to supercede previous models, simply 220 built.
-Morris CS9: Morris was a prolific prewar car manufacturer, only only produced 99 of its own armored motorcar in 1938-39, the CS9. A sturdy iv×4 lightly armed and armored, it was apace retired from the front end line.
-Morris Light Reconnaissance Car: Designed and mass-produced afterward Dunkirk (1940) at 2200 units, this lite RC armored motorcar was lightly armored and protected, simply cheap to congenital and faster than the heavier CS9. Yet it suffered from reliability issues and had limited offroad capabilities.
-Standard Beaverette: A desperate case of improvization, these were post-Dunkirk 1940. Chosen "Lord Beaverbrook's pets" (RAF) they were hastily-fabricated armored conversions for home guards defence. They were made of Standard car vehicles, 2,800 converted in a shot time and several serial. They only served at Habitation.
Lite tanks
Vickers Light Mk.II-3
Mk.I (x built), Mk.II (66 congenital) and Mk.Iii (34 congenital), 110 built in all. From these calorie-free tanks derived many models, including the 6-ton light tank widely sold for export. They were classified as cavalry tanks, light, fast, with a turret armed with a single gun, and a coiffure of two. Relegated for preparation until 1942.
Vickers Lite Mk.IV
34 of these improved Mk.IIIs with a new hull and suspensions were delivered.
Vickers Lite Mk.V
22 of these 3-men coiffure vehicles with a redesigned hull were congenital.
Vickers Calorie-free Mk.Six
1682 congenital. By far the nigh common light tank of the BEF, the Mk.VI was produced until 1939, of which many were sent overseas. It used a heavy .50 cal (12.seven mm) machine gun, combined with a light auto gun (7.seven mm/0.3 in).
Tetrarch (Tank, lite, Mk.VII)
177 built. The A17 was a specific wartime version designed to be airborne. The Tetrarch served in Normandy, just, being unsatisfactory, they were quickly withdrawn. Next, was the Harry Hopkins, a disastrous model.
Tank, light, Mark VIII "Harry Hopkins"

The Tank, Light, Mk Viii (A25), improve known equally "Harry Hopkins", was a British calorie-free tank made in just 100 vehicles past Vickers-Armstrong specifically for airborne operations. Information technology was also the very last of the long line of British light tanks and successor to the Mk VII Tetrarch. Compared to the latter, it was larger and had a better armour. Submitted to the War Office in tardily 1941, the design was accepted and an order for 1,000 was approved by the Tank Lath (War Office), later increased to two,410 in November 1941. However production but started past June 1942 and early on exercises underline a smashing number of problems, requiring a stray of modifications of the design as product was ongoing. Complaints accumulated at the War Function from the Fighting Vehicle Proving Establishment. The problems were such that only vi Hopkins tanks had been delivered past mid-1943, and the serie went on until reaching 100 in February 1945 before being cancelled.
Past mid-1941 already, some in the War Function and British Ground forces estimated that calorie-free tanks were no longer desirable, defective armament and armour, and often foreshadow in their scout role by cheaper armoured cars. In general they performed poorly in many engagement. For the Mk VIII this meant they were already undesirable and were in addition obsolete when the product ended. In fact none ever saw combat. Reconversion plans were made by the War Function like having reconnaissance units fielding these, attached wings tests, to exist towed as gliders, simply null really worked. By default of other ideas, they were handed over to the Royal Air Forcefulness, and used use in airfield defence. The Mk VIII just variant was the short-lived Alecto cocky-propelled gun, using a howitzer for paratroopers close-support artillery in airborne operations, but only a few were produced, only tested, never fielded in active units.
Medium tanks
Cruiser Mk.I, A9
125 built in 1938. Designed in 1937, a evolution of Major Giffard Le Quesne Martel'south tankettes, these medium tanks were the forerunners of the famous Crusader.
Cruiser Mk.II
175 congenital. Closely derived from the Mk.I, it was equipped with a 2-pounder (37 mm/ane.47 in) high-velocity gun, a heavy Besa machine-gun and a coaxial Vickers motorcar gun.
Cruiser Mk.III
65 congenital. Derived from the Mk.Two, this new medium tank had a Christie pause, giving it a much better grip on rough terrain. They were built in part for the BEF, but apace supplanted past the Mk.IV.
Cruiser Mk.IV
890 in all (225 Mk.4 and 665 Mk.IVA). Based on the Mk.Three with improvements merely with a far superior, sloped armor. It was widely used in Due north Africa .
Cruiser Mk.Five Covenanter
1771 congenital in 1940-42. A largely improved Cruiser, built by LMS/Nuffield, which suffered from many pattern flaws, despite being the pattern of the Crusader. It saw petty combat and was generally used for drilling.
Cruiser Mk.VI Crusader
5,300 in all. An all-around superior tank to the previous Cruisers, it made up the bulk of the British tank force during the African campaign. Merely, suffering from engine issues, relatively weak armor and armament, it was phased out in 1942.
Cruiser Mk.Vii Cavalier
500 built. Also known earlier every bit the Cromwell I or A24 (Nuffield), it was basically an improved Crusader with a new turret, armor and vi pdr.
Cruiser Mk.VIII Centaur/Cromwell
four,016 built until 1945. Improved version of the Cavalier or A27L (the Centaur was at beginning known as the Cromwell II) with a Freedom Engine (by Nuffield). The Cromwell proper (A27M) was propelled by a more powerful Rolls-Royce Meteor, an accommodation of the famous Merlin propelling the Spitfire.
Cruiser Mk.8 Challenger

This 1942 projection, headed by Roy Robotham, was meant to carry the long 17-pdr gun. On paper, this was quite a formidable anti-tank gun, merely incompatible with the turrets of the Crusader and Cromwell series. It was realized that the new tanks (Comet and after Centurion) would need at least two more years of development, so an interim solution was chosen with the modification of a Cromwell tailored to carry a larger turret ring for the 17-pdr.
This resulted into the A30 design, basically a stretched-out Cromwell with an extra pair of roadwheels and many other modifications, including the removal of the bow machine gun to complimentary space for the bigger rounds. The new turret was taller and, due to the strain added, compromise led to information technology having thinner armor than actually plant on the Cromwell. Afterward production started in February 1943, with 200 Challengers built by Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Visitor, the Full general Staff declined any further order and canceled the project in Nov of that year. The few Challengers built acted as tank hunters until the end of the war. They arrived in operations in August 1944 in Normandy, and then northern France and the Low Countries. Many served with the 1st Czechoslovak Armoured Brigade and 22 were found in service in the Czechoslovak army until 1951 when provisions of Soviet-built tanks made information technology obsolete.
Derivative: The A30 Avenger tank hunter
The Challenger's turret problems were later to exist solved by a tank hunter, developed in 1944 by Leyland motors. It reused most of the Challenger, swapping to the Comet'due south suspensions in late production (1945). This peculiar vehicle was the A30 self-propelled gun, Avenger. simply like the Achilles, a conversion with the 17-pdr of the American M10 GMC Wolwerine, the Avenger had a lower, thicker open top turret, which just a pocket-sized encompass for the coiffure. It was not very successful and of the 230 ordered, it seems but nearly 60 were delivered as the order was cancelled in May 1945. None was used during the war, only they made two tank hunter battalions until 1952, discarded subsequently.
Comet
1,186 built in 1944-45. A product of Leyland motors, carrying the 77 mm (3 in) gun, better known as the legendary 17-pdr, the best piece of AT ordinance in the Allied arsenal by 1943. The Comet was also designed to right the Cromwell'southward flaws (rails shedding and broken suspension problems).
Infantry Tank Mk.I Matilda I
140 built. This vehicle was slow and very well protected, with a simple caliber .303 (7.62 mm) heavy automobile gun, it was a testbed for the next, better known Matilda Two.
Infantry Tank Mk.2 Matilda 2
2,987 built by 1939. Called A12, Tank, Infantry, Mk II, it was a major best-seller among the British models. By 1939, about 300 were produced. They were a little faster, had a powerful and economical diesel and a high-velocity 2-pounder gun (forty mm/ane.57 in). It was twice every bit massive and overall ameliorate protected than the Matilda I. Heavy tank by the standards of 1939.
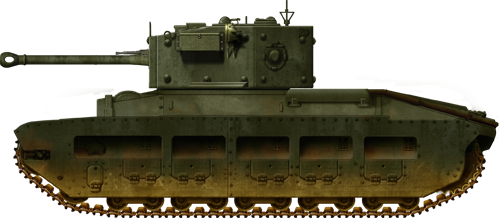
Matilda Black Prince, click the flick for more.
Infantry Tank Mk.3 Valentine
8,300 built until 1943. Designed internally past Vickers without a specific request from the War Ministry building, the Valentine infantry tank was more than compact and lighter than previous tanks of the type. It was not a priority, but received the endorsement of the War Office later the Dunkirk evacuation, beingness produced in many versions, steadily improved until the Mk.Xi of 1943.
Infantry Tank Mk.4 Churchill
7,368 built. The Tank, Infantry, Mk.Iv was i of the heaviest, simply as well most undecayed Centrolineal tanks during the state of war. Its sturdy chassis and well-protected hull served for many conversions and utility versions: bridge layer, minelayer/minesweeper, AVRE (Royal engineer corp), Petard (mortar), Oke and Crocodile (flamethrower), ARV (recovery), ARK (ramp).
Others
Bishop SPH back up artillery
149 built in 1941. Converted Valentine with a protected QF 25-Pdr (87.6 mm/3.45 in) howitzer
Archer SPG tank hunter
660 congenital. Tank hunter armed with the 17 Pdr gun on the Valentine chassis, 1944.
Sherman Firefly
ii,000 built. Tank hunter armed with the 17 Pdr (76.ii mm/three in) gun on the Sherman chassis, 1944.
WW2 British Tanks more in detail
(And Tanks missing as posts for now).
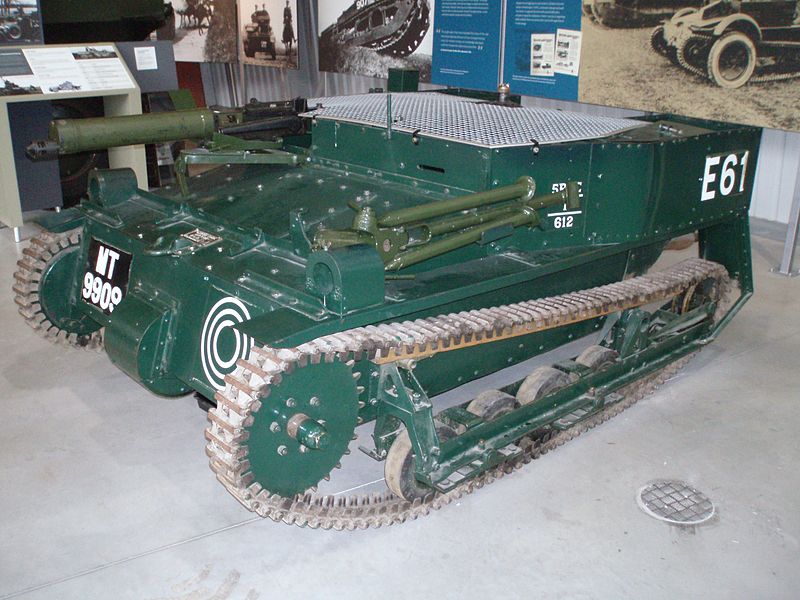 The Vickers Carden Loyd Mark.VI was the most exported and most produced tankette, from 1927 to 1935. Born as a concept from ground forces engineer Major Giffard LeQuesne Martel, information technology reduced the armored mobility concept to its very core. 450 were congenital, most exported, although many served with the British armored forces. They were discarded and phased out to training duties past 1939. The tankette fad lasted until 1939. Photo credits: Flickr, dave Highbury, Bovington Tank Museum (wikimedia commons)
The Vickers Carden Loyd Mark.VI was the most exported and most produced tankette, from 1927 to 1935. Born as a concept from ground forces engineer Major Giffard LeQuesne Martel, information technology reduced the armored mobility concept to its very core. 450 were congenital, most exported, although many served with the British armored forces. They were discarded and phased out to training duties past 1939. The tankette fad lasted until 1939. Photo credits: Flickr, dave Highbury, Bovington Tank Museum (wikimedia commons)

The Vickers 6 ton (Mark East) from 1929. With its twin turret and one turret versions, it was another one of the firm'south outstanding consign successes. 13 countries bought it. The first customer, the USSR, developed the T-26 and the Polish business firm Ursus developed the 7TP. Here is a Portuguese Vickers Mark E Type B (37 mm/i.46 in)

The Vickers Medium tank Mk.I was another famous interwar British tank. It belonged to the early twenties generation, fitted with a full traverse three-man turret (for the first time in the earth), a new interruption organization, and a quick-firing three pdr (47 mm/1.85 in) gun. 200 were built and phased out for training in 1938. The side by side Medium Mk.Ii was by and large similar. Production stopped in 1934. Many were reactivated and served in secondary duties during the early phases of WW2. They were slow, desperately protected and their interruption too weakly congenital to sustain any damage.

Probably the most successful of all tankette derivatives, the famous "Universal Carrier" was mass-produced to such an extent that information technology became the prime scout and armored mover of all Commonwealth forces, existence largely supplied to the Soviets (like in this picture), Gratis Polish, Complimentary French and other allies during World War Two. It was very fast, reliable, but lightly armed and protected only against small artillery fire. Information technology was also produced and used in big numbers by the Canadian ground forces.

The Matilda I was a new generation specialized infantry tank. But this cost-saving model was speedily replaced by the much more efficient Matilda 2, which became famous during the early phase of the war (1940-42) in Africa. Although very slow, its armor could stand against everything except the mortiferous German 88.

Conceived equally the Tank, Infantry, Mk. III, the Valentine was a compromise between the speed of the Cruiser Four and the sturdiness of the Matilda Two. It was declined into eleven versions throughout the war, with a total product of 8275, the biggest British wartime tank product always.

The Churchill was the last infantry tank. This skilful all-around heavy tank was at the forefront of the British armored strength from 1943 to 1945. It started with teething problems in 1941, and failed miserably at Dieppe. However, in Tunisia, this model proved its superb climbing abilities and out of the ordinary sturdiness. It was used for any kind of support and genie missions imaginable.

The Cruiser I was the first of a long line of early cruiser tanks, a new breed of cavalry tanks designed to exploit a breakthrough. Unfortunately, their height speed was unsatisfactory since they had a classically sprung suspension. The upwardly-armored Cruiser Mk.Ii, was likewise slow to operate effectively equally a cruiser, but the Mk.III and Mk.IV, featuring a Christie-manner suspension, were a real improvement and regained the edge.

The Cruiser Mk.4 was very similar to the Cruiser III, autonomously from the turret design. Very fast, information technology appeared ideally suited for desert warfare.

The Cruiser V Covenanter (named after the Scottish Presbyterian movement) was a much-improved evolution of the Mk.IV. Production was showtime ordered in Apr 1939, featuring innovations like an opposed-piston engine, the front placement of cooling radiators, and the broad use of welding for the hull construction. All the same, it was kept importantly for training, and inspired the more famous Cruiser VI.

The Cruiser VI, better known every bit Crusader, was the nigh famous cruiser tank using the revolutionary Christie pause. Its tiptop speed largely compensated for its light ammunition and boilerplate protection. It was, even so, the war horse of many operations throughout the N African campaign, and 1 of its most distinctive symbols.

Although like, the Cruiser 8 Centaur and Cavalier differed by the choice of their engine. They had a new QF half-dozen-Pdr (57 mm/2.24 in) gun and proficient protection, while retaining a low profile and excellent speed of previous cruisers.
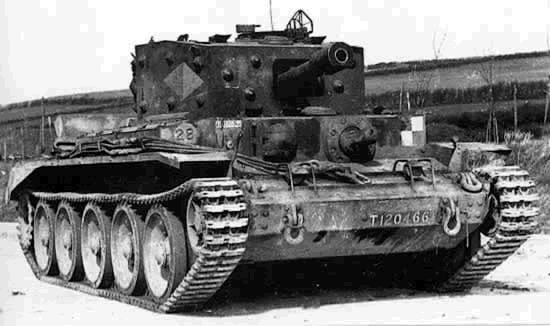
The Cruiser VIII Cromwell was the i fitted with the Rolls Royce Meteor engine, and most successful of the iii. It was introduced in 1943, declined into many variants. It soldiered until the end of the state of war.
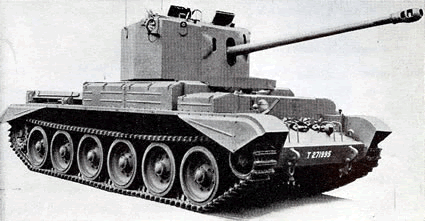
The Cruiser Eight Challenger was based on the previous Centaur/Cromwell, merely fitted with a devastating 17-Pdr (76.2 mm/iii in) gun. Although promising and liked past its crews, it was dropped in favor of the Sherman Firefly.
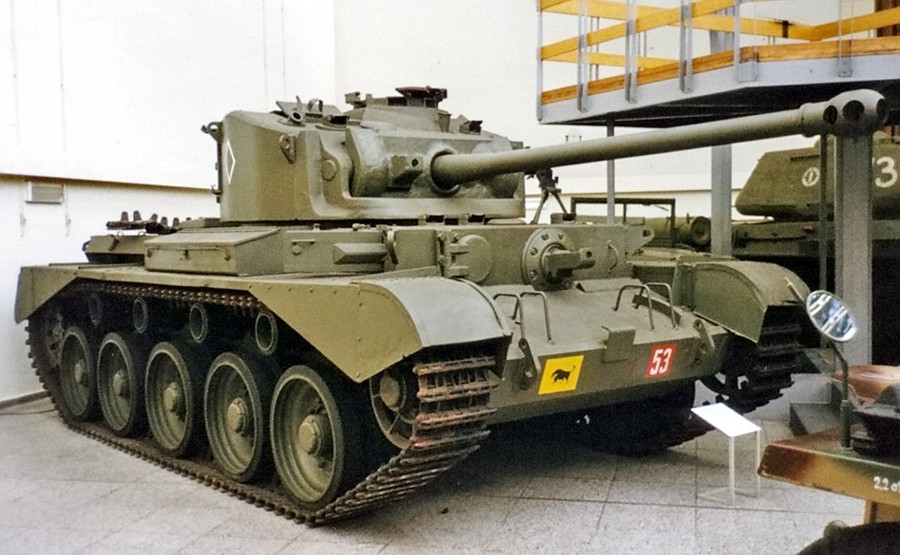

Adult after a long line of Crusader successors, the Comet was the last of this "cruiser" generation, and the best overall. It arrived in belatedly 1944, ready for postal service D-Day operations in Europe, and opening the way for the postwar generation of British tanks led past the legendary Centurion.
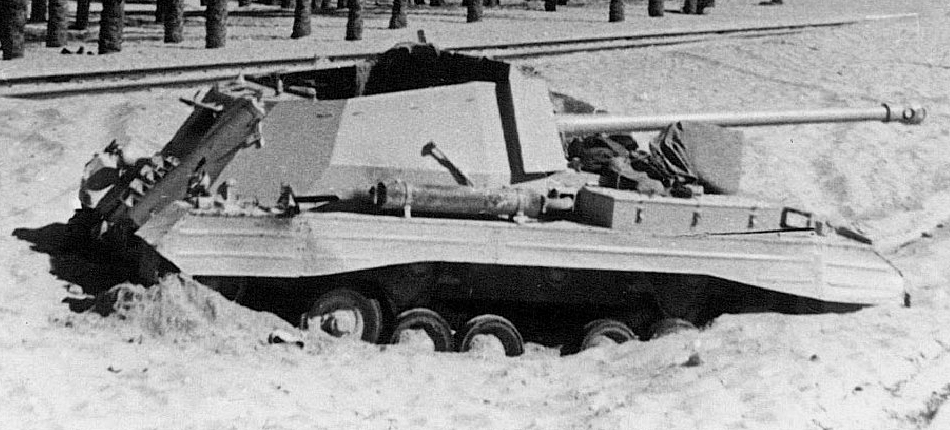

The 17 pdr (76.ii mm/three in) Archer, built over surplus Valentine chassis, was a British SPG tank destroyer. Information technology was designed to brand use of the 17-Pdr in its original course, but had it mounted facing the rear of the tank.
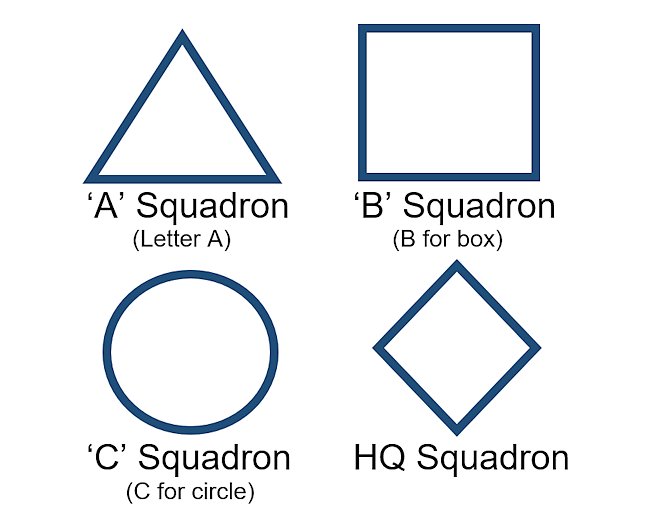
British tank squadron markings. The colour changes depending on the regiment, just they commonly used the same shapes.
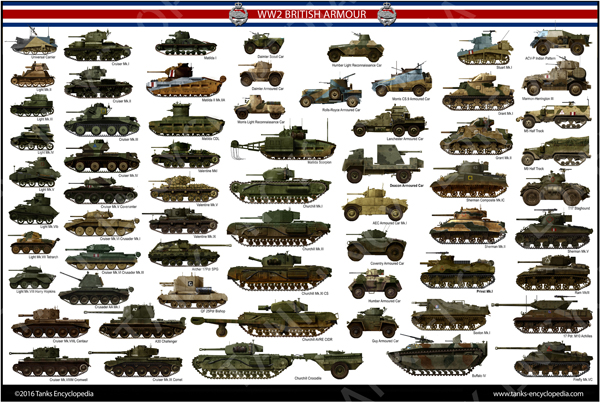

British Tanks of WW2 Poster (Support Tank Encyclopedia)
Illustrations

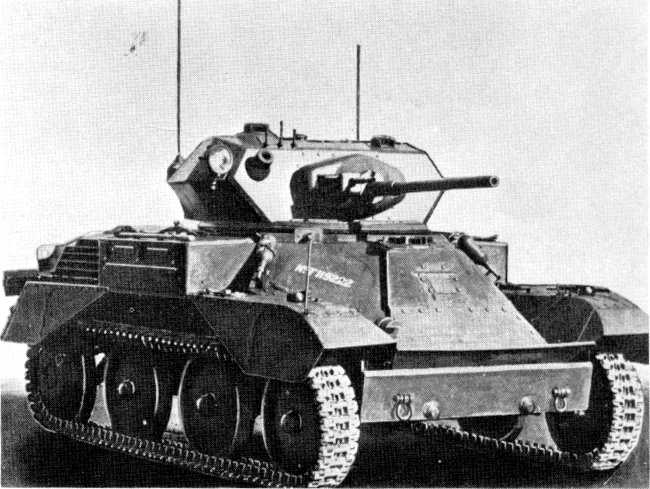
The turret of this Canadian 12th Manitoba Dragoons Staghound Armored Car was fitted with iv 60 lb RP-three (Rocket Projectile 3-inch) air to footing shipping rocket launcher rails in November 1944.
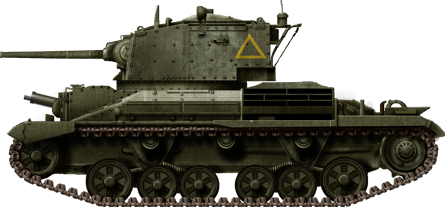
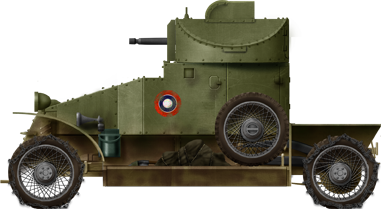
A10 Cruiser Mk.Two in early configuration, with three .303 (7.62 mm) Vickers liquid-cooled automobile-guns. It was part of the 21 delivered which were later sent with the British Expeditionary Strength (BEF) to fight in France.
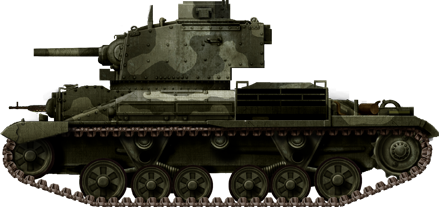
Cruiser Mk.IIA CS (Close Support) with the BEF, 1st Armoured Partitioning, French republic, May 1940.
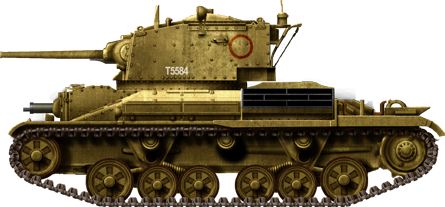
A Cruiser Two defending Tobruk, during the aftermath of the Italian invasion in December 1940.
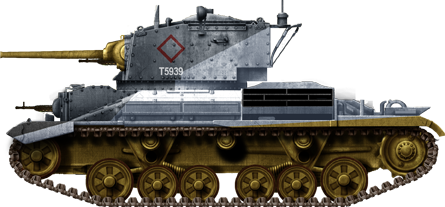
A Cruiser Mk.IIA (Besa machine-guns) during Operation Compass, the British counter-offensive confronting Italian forces in Great socialist people's libyan arab jamahiriya, January 1941. The last surviving Mark IIAs were phased out past tardily 1941.
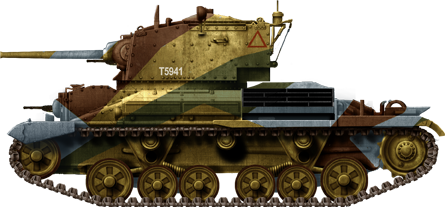
A10 Cruiser Mk.IIA in Greece, third RTR, April 1941. 60 were shipped from Due north Africa to Southern Greece to back up the Greek defenders confronting much superior German Forces.

Cruiser Mk.Iii during the French campaign, B Squadron, 3rd Battalion, Royal Tank Regiment, 3rd Armoured Division, May 1940.

Cruiser Mk.Three of the 7th Royal Tank Regiment, 7th Armoured Brigade, Operation Crusader, Libya, December 1940
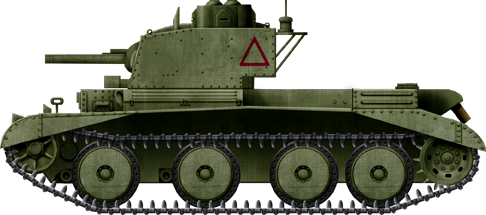
Cruiser Mk.III CS (Shut Support)

Cruiser Mk.Four from the tenth Hussars, 2nd Armoured Brigade, 1st Armoured Division, BEF, 1940

Cruiser Mk.IVA, B squadron, 7th Queens Own Hussars, Libya, 1941
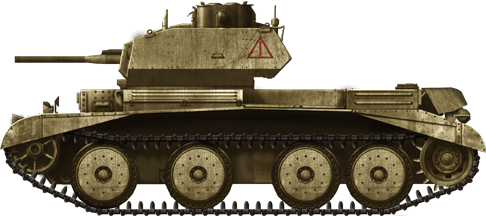
Cruiser Mk.IVA, seventh Armoured Segmentation, Egypt, 1941.

Cruiser Mk.IVa, Greece, 1941.

Cruiser Mk.IV, 7th Infantry Brigade decoy force, Republic of cyprus, 1942.

Covenanter Mark I, early on production version, summer 1940.

Covenanter Mk.I CS

Covenanter with a brown livery, 18th Hussars, ninth Armoured Sectionalization, 1941-42.

Covenanter Mk.Ii

Covenanter Mk.III in North Africa, King's forcefulness, fall 1942.

Covenanter Mark III, belatedly production version, 9th Armoured Sectionalisation, 1943.
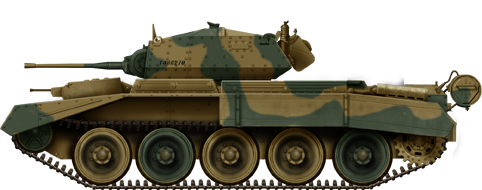
An early production Crusader Mk.I, Libya, Functioning Crusader, Nov 1941.

A Crusader Mk.I CS (Shut Support). These converted versions were equipped with a 3.7 in (94 mm) L15 howitzer firing fume rounds. Gazala, December 1941.

Tardily Crusader Mk.I. These models incorporated modifications gained from early desert war experience, like a slightly ameliorate ventilation system, to try to prevent the engine of overheating, and improve, full side, fixed protective panels.

A Crusader 2 of the 9th Queen Lancers, attached to the 1st Division, Great socialist people's libyan arab jamahiriya, December 1941. Too the new protective panels and some pocket-sized alterations, the Mark Ii were pretty shut to the previous Mark I. They even retained the auxiliary forwards turret, usually removed soon later arrival on the forepart.

A Cruiser 6 Crusader Mark II of the 22nd Armoured Brigade in Libya, Dec 1941. This three-tone pattern was rare.

Late production Crusader Mk.II. Unknown unit, Gazala, May 1942. By the outset of the 2d battle of El Alamein, nigh all Marker I and IIs had been removed from the frontline, replaced by more than recent Mark IIIs.

Crusader Mark III from the 6th Armoured Sectionalisation, February 1943, showing a green pattern with night light-green, composite stripes. Crusaders were often painted "on the spot" with available colors and depending on the flavour and landscape, every bit there were few regulations on this matter.

A Crusader Marker III, 1 of the but 100 which fought in October 1942 during the second boxing of El Alamein.

Cruiser Six Crusader Three of the 17th/21st Lancers, 6th Armored Partition, Tunisia, November 1943.

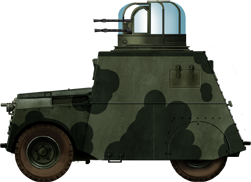
Over 1373 Crusaders were converted for special purposes, of which around 400 were Crusader AA Mark Is. They were armed with a Bofors 40 mm (ane.57 in) gun, bringing its highly recognizable "pom-pom" audio on the battleground, which gave information technology its pop surname amid soldiers and Royal Navy sailors as well. This was the offset conversion of existing Mk.III hulls. At showtime, the gun was just mounted on an open up platform with its regular forepart flat shield. But information technology soon became obvious that better protection was needed and a four-side, open-acme shield was wrapped around for the next batch of late production models.

A Crusader AA Marking Iii, with its distinctive twin 20 mm (0.79 in) Oerlikon mountain. It had a devastating combination of speed and firepower, peculiarly mortiferous for low-flying aircraft. They were coupled with a targeting .303 (7.7 mm) Vickers machine gun. These guns were counterbalanced by a big metal cylinder mounted on a threaded rod, for aligning. They could fire most vertically. The Marking II and Three only differed by the radio position, moved from the turret into the hull, for added gratuitous space. They were put in use in the later on stages of the African campaign, in Tunisia, and fought in Sicily, Italy and Normandy. There, Allied air potency was such that they were relegated to secondary duties. Product records are scarce but, in June 1944, 268 of these Mk.2/IIIs were enlisted for D-Day. Showtime tests began in June 1943, and conversions started in October. Normal provision was 600 rounds.

Standard Cavalier used for training in Great britain, fall 1942. The Cavalier was basically an up-armored and redesigned Crusader. The engine and transmission as well-nigh of the technical parts were identical. The easiest points to distinguish the Condescending from the Centaur and Crowmell are the redesigned rear (due to the transmission), positioning of the rear extra fuel tanks, and absence of the exhaust vent on the engine deck backside the turret.

A24 Cavalier with mudguards, from a training unit of measurement in Britain, 1943. In that location is a mislabeled "Condescending" at the Saumur Museum, with a biscuit-dark brown cover-up pattern and agile units symbols, which in reality could be a Centaur or Cromwell CS. Since a few "Cavaliers" were donated to the French forces in 1945, this is probably the origin of the mistake.
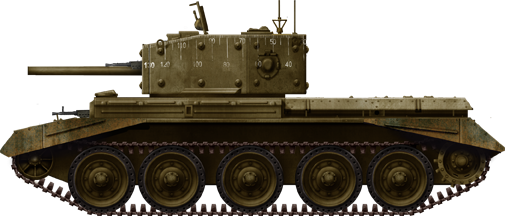
Cavalier OP (Observation post), Great Britain, 1944.

Cavalier ARV (Armored Recovery Vehicle) in Holland, 1945.

Centaur Marker I, Great United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland, December 1942.

Centaur Mark Three, training unit of measurement in Great Britain, mid-1943.

Shine Centaur III of the 14th Jalzowiecki Lancers Regiment, 16th Independent Armored Brigade, in a preparation unit in Great Britain, May 1944.
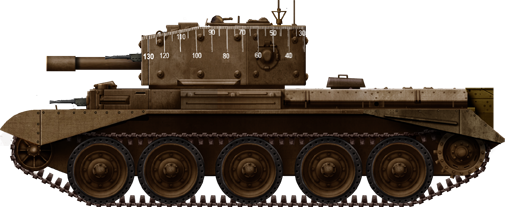
Centaur IV CS (Close Support), Normandy, summer 1944.

Camouflaged Centaur Iv CS, equally preserved at the Saumur tank museum.

Centaur Mark I AA, Normandy, July 1944.

Centaur ARV Dozer of the Royal Engineers, summertime 1944.

Infantry tank, Mk.I (A11). The first Infantry Tank was completely overshadowed past the Marker Ii, a completely unlike model, better known as the Matilda. This designation is ofttimes incorectely used as a nickname for the awkward, duck-tail await of the first infantry tank.

Infantry Tank Mk.I, 1st Ground forces Tank Brigade, defence force of Arras, 15 May 1940. This unit of measurement fought confronting Panzer IIIs and IVs of full general Rommel\'southward 7th Panzer Partition. Many surviving Matildas were left in French republic, most sabotaged, earlier and during the evacuation of Dunkirk.

The A11E1, the pilot model for the Infantry Tank Mk.I, here on trials.

Tank Encylopedia'due south own rendition of the AE1 Independent.
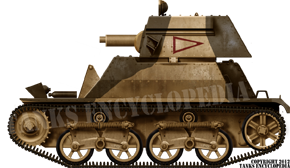
Light Tank Mk.IIA, unknown unit, probably Australian, East Africa, Baronial 1940. 
Light Tank Mk.IIB Indian Pattern, here with a recognizable square cupola, better engine, amend hull cooling and a more powerful Meadows EPT 85 hp engine.
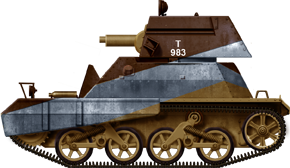
Light Tank Mk.Two, 6th Australian Cavalry Partitioning – Arab republic of egypt, 1941.

Calorie-free Tank Mk.III, the last of this lineage derived from the Mk.VI tankette.

A4E19 image.

Regular Light Tank Mk.4, Great Uk, 1939.

Early Light Mark V derived from the L3E1 prototype in 1934. The Horstmann suspension system was virtually unchanged.

Light Mark V, fully equipped, possibly used by the BEF for grooming in French republic, prior to May 1940.
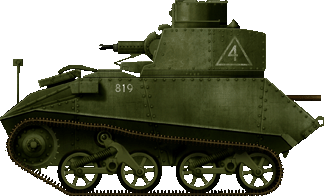
Light Tank Mk.Half-dozen, offset batch vehicle, early 1937. Only a scattering of these were produced, perhaps 30 or 40, and they were probable used, after 1939, equally training machines, similar the Mk.Vs.
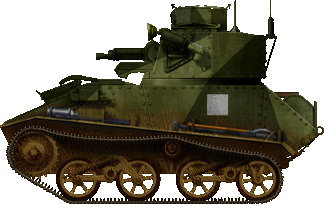
Light Mk.VIa of the British Expeditionary Forcefulness (BEF), western Belgium, May 1940.
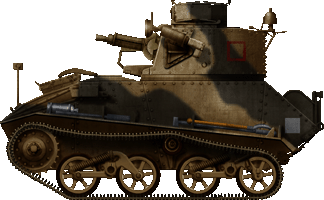
Vickers Mk.VIa Light Tank, B Squadron, 4/7th Royal Dragoon Guards, BEF, northern France, February 1940
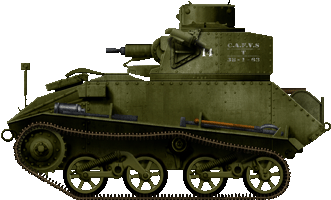
Low-cal Mk.VIb of a C.A.F.Five.T (Canadian Armoured Fighting Vehicle Training) unit, late 1940.
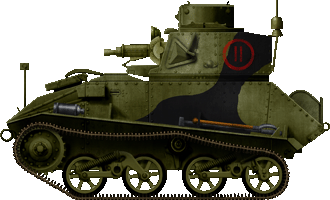
Light Mk.VIb of the 11th troop, C squadron, 2nd Royal Tank Regiment, French republic, May 1940.
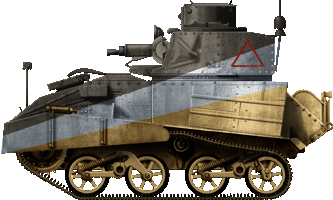
Light Mk.VIb, A Sqdn, 1st Battalion Royal Tank Regiment, 7th Armoured Division, Egypt, fall 1940.

Light Mk.VIc, Malta, June 1942. This late version, produced until mid-1940, was reequipped with a high-velocity xv mm (0.59 in) Besa machine-gun. The Besa heavy machine-gun had a better punch and accuracy than the Vickers cal.50 (12.7 mm). However, it also had poorer performances compared to the German 20 mm (0.79 in) that equipped the Panzer Two. Its unusual method of cocking was tricky and needed careful maintenance.

The commencement Vickers Marker Es were model As, the twin turret model, armed with two liquid-cooled Vickers automobile guns. This one was part of the only four machines retained by the British ground forces for testing and training purposes. Many Type A vehicles were sold away, only they were by far eclipsed by the Type B.

An early production Vickers East Type B, with the low-velocity 47 mm (1.85 in) gun. This i served with the Siamese ground forces, which bought thirty Blazon Bs in 1933-34. They saw action in 1941 against French colonial forces, and duelled with the few French calorie-free tanks they encountered.

Bulgarian Vickers Mark F. Bulgaria bought twenty Mk.Fs, a modified version of the Marking Eastward, mostly for training purpose. They were still in service at the outset of WW2.

Finnish Vickers Marking F, modified with a Bofors 37 mm (i.46 in) gun. They only took part in one boxing until the very end of the war with Russia in 1939.

Archer Self Propelled 17 pdr, Valentine, Mk I, Archer in Italy, winter 1944-45.

Archer in kingdom of the netherlands, winter 1944.

British Archer, east bank of the Rhine, 1944-45.

An AEC Mk.I Gun Carrier Deacon with an early greenish inconspicuous livery, December 1942.

Standard AEC Mk.I Gun Carrier Deacon in desert livery, 1943.

Early Mark VI model. Information technology was an open model, completely unprotected from to a higher place. Afterward a complete redesign, the model concluded every bit the famous "Universal carrier"

The main production model, besides the nigh exported and built nether license. It was, this time, completely protected from above, with ii hexagonal domes for the crew members.

The late product model, just retained past the British army, and congenital by the Royal Ordnance Factory.

A Carden-Loyd Mk.VI of the Royal Thai army, January 16, 1941, Burapha Siamese army, boxing of Phum Preav. 30 tankettes of the 1930 type and perhaps 30 others were purchased in 1935.

Belgian SA FRC 47mm, tank hunter, self-propelled gun. The Belgian Commission permanente de Motorisation purchased 6 tankettes of the Marking VI blazon in 1929, but they converted them into SPGs, equipped with the standard-upshot S.A. 47 mm (one.85 in) built at Fonderie Royale des Canons (FRC), Liege. Information technology was found more practical and effective to carry than to tow these guns. They were part of the Chasseurs Ardennais until 1938, and then spread into two Régiments Cyclistes-Frontière, which ambushed a German column on May ten, 1940, alongside the Meuse river.
.png)
Captured Dingo Mk.I, designated Leichter PzKpfw Mk.I 202(e), DAK, Great socialist people's libyan arab jamahiriya, 1941.

Dingo Mk.IA, British Expeditionary Force, 3rd RTR, 1st Armoured Division, Holland, summer 1940.

Dingo Mk.IA from the HQ squadron of the 1st Northamptonshire Yeomanry, 20th Armoured Brigade, 6th Armoured Division, preparation in Great Britain, 1941.

Dingo Mk.IA, Libya, fall 1940.

Daimler Dingo Mk.IB, United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland, fall 1941.

Dingo Mk.II, unknown reconnaissance unit, Western Europe, 1944.

Dingo Mk.II, 4th Field Squadron RE, 7th Armoured Division, Libya, 1942.

Dingo Mk.Ii fastened to the reconnaissance battalion of the seventh RTR, VIIIth Army, Libya, fall 1942.

Dingo II, 2nd NZ Sectionalization HQ, El Alamein, November 1942.

Dingo Mk.2 with a Boys AT rifle, 23rd Armoured Battalion, 5th RTR, Tunisia, March 1943. (Hard disk drive illustration)

Dingo Mk.2, NZAC grooming heart near the Scarlet Sea, 1945.

Dingo Mk.Two, 11th Hussards, 7th RTR, Holland, winter 1944-45.

Dingo Mk.Iii, 11th Armoured Division, Holland, winter 1944-45.

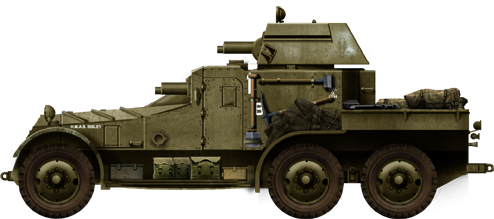
AEC Marker I, El Alamein, November 1942.

AEC Marker Ii, 10th Indian Infantry Division, Italy, 1943.

AEC Marking II, Italy, wintertime 1944 (now preserved at Bovington).

AEC Marking Ii used by the Yugoslav Army in 1945.

AEC Marking III, D Squadron, 2nd Household Regiment, VII corps, Normandy, 1944.
![]()
AEC Mk.Three, second British Army, North-W Europe, spring 1945.

Coventry Armoured Car, early production version on trials, summertime 1944.

Coventry in French service, second Tunisian Spahi, fifth Cuirassiers, Indochina, 1947-52.

A Guy Armoured Car in 1939. It was the predecessor of the Humber Mark I.

Humber Mark I, Northward Africa, 1941.

Humber Marker IA, Keen United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland, 1942
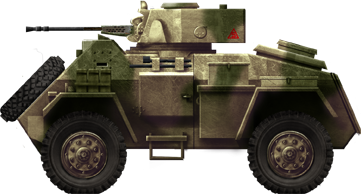
Humber Mark II, Italy, early on 1944.

Canadian Humber Mark Ii in France, mid-1944. Notice the .fifty cal's short barrel.

British Humber Marking III in Tunisia, early 1943.

Humber Mark 3 attached to the recce battalion of the 1st Polish Armoured Division, Normandy, June 1944.

Humber Mark IV "Laughing Boy III", from a British unit, Kingdom of the netherlands, fall 1944.

British Humber Mark Four in the Rhineland, wintertime 1944-45.

Lanchester armored motorcar from the RNAS (Royal Naval Air Service), Dunkirk, 1915.

A camouflaged Lanchester, Flanders, 1916.

RNAS operating in Persia, 1916.
Russian Lanchester, Caucasus 1916. Observe the 37 mm (1.46 in) Hotchkiss, the small cupola above the turret, the absence of stowage boxes at the rear and the tires wrapped in mud bondage in autumn.

A Lanchster Mark I of the twelfth Lancers. This was a heavily armed vehicle for the time, armed with a heavy MG and two Vickers medium MGs. The first could destroy lite tanks when equipped with AP bullets.
A vehicle of the 12th Lancers, B squadron in Malaya, 1941. This particular vehicle (now on display in a museum) was reequipped with a Calorie-free Tank Marker Iii turret and had only ii Vickers 0.iii in machine guns. The Lanchester six×four had good off-road capabilities and was rugged and reliable. Withal, it was too heavy and deadening for effective operations in reconnaissance units.

Morris CS9 of the twelfth Lancers, British Expeditionary Force (BEF), Franco-Belgian borderland, May 1940.

Morris CS9 of the 11th Hussars, Great socialist people's libyan arab jamahiriya, 1942.

Morris Mk.I, early production version, Uk, 1941.

Morris Mk.I in Northward Africa, now preserved at Bovington.

Morris LRC Mk.Ii in Normandy, summer 1944.

Morris LRC Mk.Two in Tunisia, RAF patrol baby-sit, at present preserved at Duxford.

Beaverette Mark I. Notice the rib going along the side of the vehicle and the vertical radiator grills.

Beaverette Mark II, with the standard camouflage. Detect the lack of the rib from the Mark I and the horizontal radiator grills.

Beaverette Mark III, early type armed with a Boys 0.5 in (12.7 in) AT burglarize.

Beaverette Mark Iii with Bren gun and "Mickey Mouse" camouflage.
Beaverette Mark III with a Boulton-Paul quad 0.iii in (vii.62 mm) turret
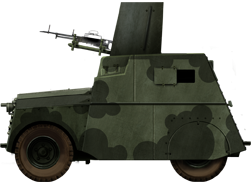
Beaverette Mark IV with a twin Vickers LMGs mountain. Observe the redesigned armor.
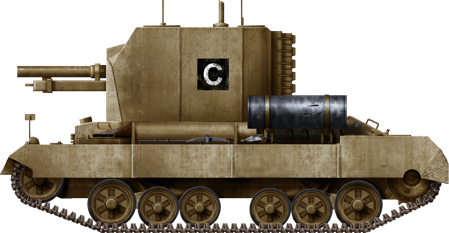
Ordnance QF 25 pdr on Carrier Valentine 25-pdr Mk 1 "Bishop" of the VIIIth Army, El Alamein, fall 1942.

Bishop of the VIIIth Regular army in Southern Italy, Feb 1944.
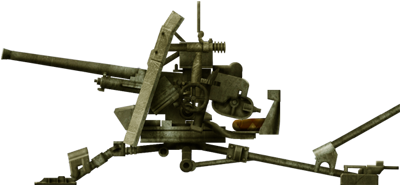
The standard 1939 two-pounder was the main infantry antitank weapon in service with the BEF in may-june 1940.
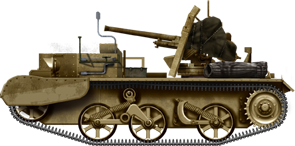
A 2 Pounder Anti-tank Gun Carrier (Universal Carrier) used by Australian forces in Due north Africa, 1941.
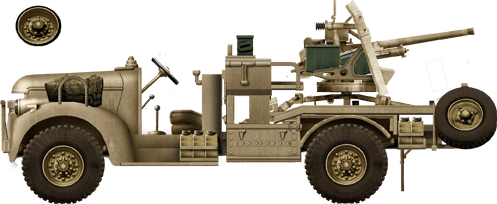
Chevrolet 30 CWT (WA/WB) 2pdr portee, the same blazon used by the LRDG in North Africa. This was a widespread solution, besides declined on the Morris 15 cwt truck, CMP Ford F30 or Chevrolet C30, until the United states of america-supplied lend-lease M10 tank hunter made them obsolete.
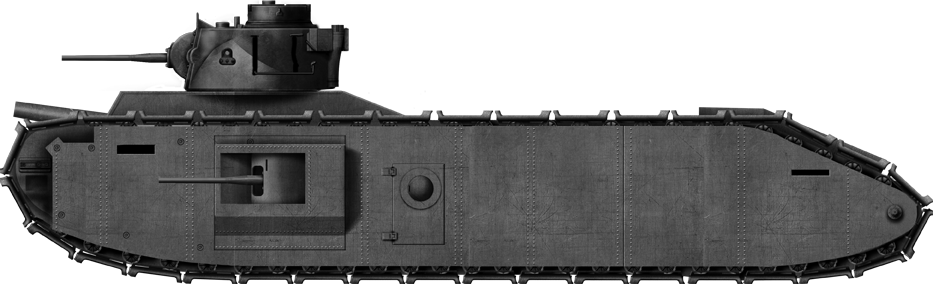
Tank Encylopedia's own rendition of the TOG-ane in 1940.

Basic AEC 4×4 ACV in UK, may-june 1941.

AEC 4×iv in North Africa, 7th armoured division, December 1941

Captured Rommel's "Max" command car. Both vehicles were called "Max" and "moritz" after popular Xix Boyish Pranks by author Wilhelm Busch published in 1865.

Dorchester in North Africa, Tunisia, 1943 with a wavy "spiked" dark brown/sand yellow pattern.

AEC 4×4 ACV in Normandy, summer 1944, observe a two-tone night light-green and olive camouflage variant in utilize until the end of WW2. When stationary, they were also oft heavily camouflaged with foliage, using the stretched canvas extensions to create a big open infinite.

A Pakistani Dorchester during the 1965 Indo-Pakistani state of war.
The 2d World War
 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Canada
Canada

 Mainland china
Mainland china
 Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
 Republic of finland
Republic of finland
 France
France
 Hungary
Hungary
 India
India
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Nippon
Nippon
 Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Poland
Poland
 Romania
Romania
 South Africa
South Africa
 Soviet Union
Soviet Union
 Espana
Espana
 Sweden
Sweden
![]() Thailand
Thailand
 The netherlands
The netherlands
 United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland
United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland
 United states of america
United states of america
 Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia

British Churchill Tank – Tank Encyclopedia Support Shirt
Sally forth in with confidence in this Churchill tee. A portion of the proceeds from this purchase will support Tank Encyclopedia, a armed services history inquiry project.
 Forgotten Tanks and Guns of the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s
Forgotten Tanks and Guns of the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s
By David Lister
History forgets. Files are lost and mislaid. Only this volume seeks to shine a light, offering a collection of cut edge pieces of historical enquiry detailing some of the most fascinating artillery and armament projects from the 1920s to the terminate of the 1940's, nearly all of which had previously been lost to history.Included here are records from the UK's MI10 (the forerunner of GCHQ) which tell the story of the mighty Japanese heavy tanks and their service during the Second World State of war.
Buy this book on Amazon!
 TOG-2R Heavy Tank Service Manual
TOG-2R Heavy Tank Service Manual
By Andrew Hills
Service Manual for the British Super-Heavy tank TOG-2R. Pieced together from surviving records this manual was written in sections during the long development of the tank and was stopped when the project was terminated. As such the transmission is incomplete but has been recreated as close every bit possible to what the original manual would have looked similar had the tank entered production.FWD Publishing
Buy this book on Amazon!
 TOG-two* Heavy Tank Service Manual
TOG-two* Heavy Tank Service Manual
By Andrew Hills
Service Manual for the British Super-Heavy tank TOG-ii*. Pieced together from surviving records, this transmission was written in sections during the long development of the tank and was stopped when the projection was terminated. As such the manual is incomplete but has been recreated as close equally possible to what the original manual would accept looked like had the tank entered production.
FWD Publishing
Buy this book on Amazon!
 The Tanks of TOG
The Tanks of TOG
The piece of work, designs, and tanks of the Special Vehicle Development Committee in World War II
By Andrew Hills
The previously untold story of the Special Vehicle Development Committee, better known as 'The Old Gang' or by the abbreviation 'TOG'. The SVDC managed in very short time to design more than than one vehicle to reach this seemingly impossible task and built tanks bearing their acronym as TOG-i and TOG-ii. FWD Publishing
Buy this book on Amazon!
Did Staghound Armored Car See Service In Sicily?,
Source: https://tanks-encyclopedia.com/ww2/gb/ww2_british_tanks.php
Posted by: fergusonsuffect.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Did Staghound Armored Car See Service In Sicily?"
Post a Comment